Oxidizing and reducing agents in organic chemistry
Data: 2.09.2018 / Rating: 4.7 / Views: 909Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Oxidizing and reducing agents in organic chemistry
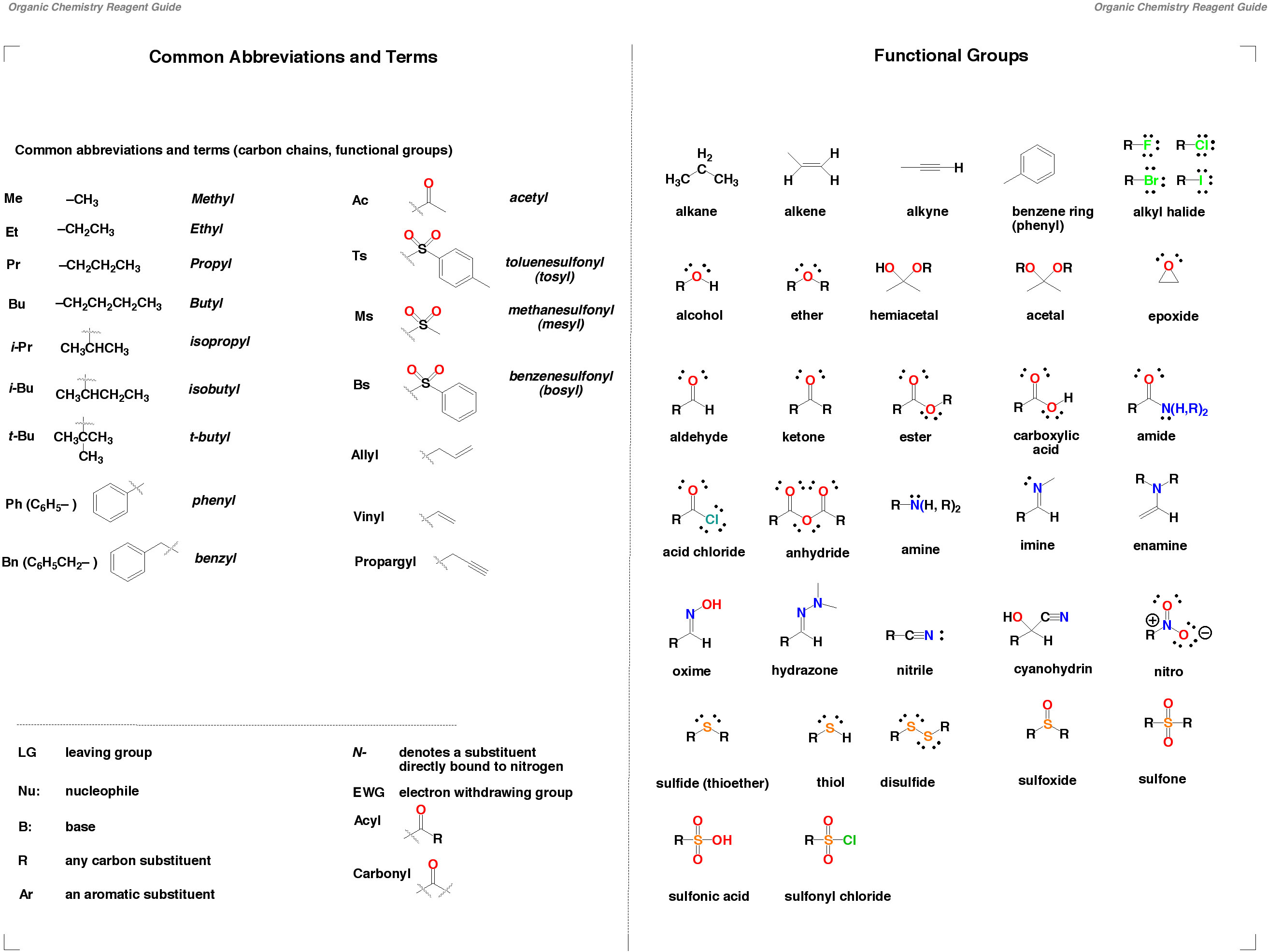
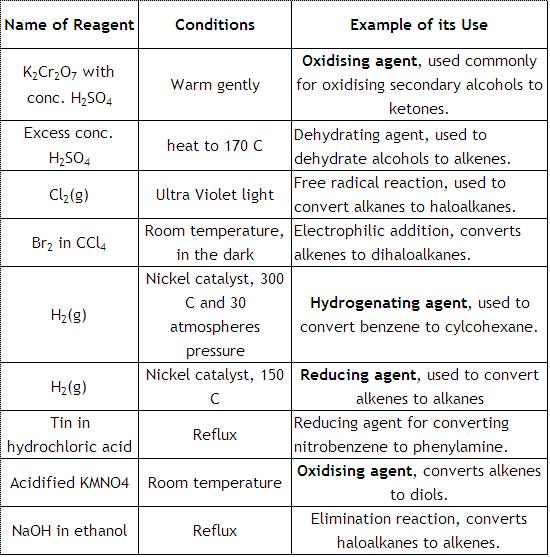
reducing agent, how to determine an oxidizing and reducing agent in a chemical reaction, and the importance of this concept in real world applications. An oxidizing agent, or oxidant, gains electrons and is reduced in a chemical reaction. In organic chemistry, good reducing agents are reagents that deliver H 2. Historically, reduction referred to the removal of oxygen from a compound, hence the name 'reduction The modern sense of donating electrons is a generalisation of this idea, acknowledging that other components can play a similar chemical role to oxygen. This page examines the trend in oxidizing ability of the Group 17 elements (the halogens): fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. It considers the ability of one halogen to oxidize the ions of another, and how this changes down the group. Consider a situation in which one halogen (chlorine, for. This is the definition of an oxidizing agent in chemistry and a list of examples of oxidizers. All of the halogens are oxidizing agents (e. , chlorine, bromine, fluorine). While an oxidizing agent gains electrons and is reduced in a chemical reaction, a reducing agent loses electrons and is oxidized during a chemical reaction. In addition, you could argue that in the SN1 reaction of Clwith tertbutyl bromide, the leaving group leaves first, reducing the oxidation state of carbon from 1 to 0, but after the attack of Cl to the carbocation, it raises the oxidation state of carbon back to 1, thus, Cl can be said to have actually functioned as an oxidizing agent here. Oxidising and Reducing Agents (1) Definition: The substance (atom, ion or molecule) that gains electrons and is thereby reduced to a low valency state is called an oxidising agent, while the substance that loses electrons and is thereby oxidised to a higher valency state is called a reducing agent. Organic Chemistry Help Redox Chemistry Organic Reducing Agents Example Question# 1: Organic Reducing Agents As a reducing agent, donates a(n) to a ketone or aldehyde. Chemistry Meta your communities Oxidizing and reducing agent. Well, it's impossible to chose, as both compounds would act as oxidizing as well as reducing agents. This, BTW, has nothing to do with the oxidation state of metal atom, which is the same in all four compounds. To reduce a molecule means to increase the hydrogen content of that molecule. In order for reduction to take place, you need reducing agents. So in this topic, we're going to explore that those different reducing agents are. In a similar way, the more weaker the oxidizing agent then the more strong is the corresponding reducing agent as shown in the figure below. Reducing Agent Examples Some of the common reducing agents includes metals such as Na, Fe, Zn, Al and nonmetals such as C, S, H 2. Oxidation is among the most common transformations in the scope of organic synthesis. As a result, the number of oxidizing agents at a chemists disposal number in the hundreds. However, the demands of synthetic chemistry dictate the synthetic chemist can always use a more specific, a more stable. An oxidizing agent, or oxidant, gains electrons and is reduced in a chemical reaction. Also known as the electron acceptor, the oxidizing agent is normally in one of its higher possible oxidation states because it will gain electrons and be reduced. In organic chemistry, oxidation is usually the addition of oxygencarbon bonds and a removal of hydrogens, while reduction is the addition of hydrogens and removal of oxygen carbon bonds. Reduction in organic chemistry is usually accomplished by a. Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Oxidizing agent (oxidant): In a redox reaction, the reactant causing the oxidation, and is itself reduced. In the combustion of methane molecular oxygen is the oxidizing agent and methane is the reducing agent. Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Reducing agent (reductant): In a redox reaction, the reactant that causes the reduction, and is itself oxidized. In the combustion of methane molecular oxygen is the oxidizing agent and methane is the reducing agent. Chem 535 Synthetic Organic Chemistry Common Oxidizing Agents for the Conversion of ROH Functionality Name Composition Typical Use Scope Limitations In chemistry, an oxidizing agent (oxidant, oxidizer) is a substance that has the ability to oxidize other substances in other words to cause them to lose electrons. Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. electrochemistry What factor determines the strength of reducing agents and oxidizing agents Chemistry Stack Exchange Find this Pin and more on Help by Jasmine Turner Young Living# . The best reducing agents are located at the bottom left of the periodic table (low electronegativity) and the best oxidizing agents are located at. An oxidizing agent (also called an oxidizer or oxidant) is referred to as a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms or a substance that gains electrons in a redox chemical reaction. oxidation and reduction in organic chemistry In ionic and free radical reactions, oxidation and reduction are defined as processes by which an element undergoes a net loss or gain of electrons, respectively. Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizing agent. It can convert secondary alcohols to ketones. It can also convert primary alcohols to carboxylic acids. 1propanol has a hydroxy group on carbon 1, so it is primary; thus it will be converted to propanoic acid. Oxidation in organic synthesis is divided into four sections: an overview of different oxidising agents used in the literature: oxidation methods used on specific functionalities in organic compounds, the use of enzymatic or microbial methods and oxidations performed under benign conditions which includes the use of enabling technologies such as ultrasound and microwave irradiation. Menu Open Menu Close Menu Close Oxidizing and Reducing Agents ChemFiles Volume 1 Article 3 Oxidation and reduction reactions are some of the most common transformations encountered in organic synthesis, and are some of the organic chemists most powerful tools for creating novel products. Reducing agents and oxidizing agents are chemical compounds involved in redox reactions. These compounds are the reactants of a redox reaction. These compounds are the reactants of a redox reaction. The main difference between reducing agent and oxidizing agent is that reducing agent can lose electrons and be oxidized whereas oxidizing agent. The oxidizing agent is a term which is used to describe a reactant in the oxidation and reduction reactions which include the transfer of electrons. Organic Analytical Chemistry Phase Equilibriums, Chemical Equilibriums, and Solutions Radiation Chemistry, Photochemistry, and Photographic and Other Reprographic Processes Learn more about these metrics Article Views are the COUNTERcompliant sum of full text article downloads since November 2008 (both PDF and HTML) across all institutions and individuals. These metrics are regularly updated to reflect usage leading up to the last few days. The Altmetric Attention Score is a quantitative measure of the attention that a research article has received online. What is the meaning of reduction and oxidation in organic chemistry? From what I learned in General chemistry OIL RIG i. e oxidation is loss and reduction is gain (of electrons). But what do we say about their usage in organic chemistry? I have seen their usage a lot of times in the form of reducing agents and oxidizing agents but never really understood it. Oxidizing agents oxidize other things, and get reduced themselves. I have an 'oxidizing agents' cabinet: it's full of compounds which contain elements in their highest oxidation state. Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Oxidizing and Reducing Agents, provides the synthetic chemist with a convenient compendium of information concentrating on the most important and frequently employed reagents for the oxidation and reduction of organic compounds, extracted and updated from EROS. The Relative Strengths of Oxidizing and Reducing Agents Common Oxidizing Agents and Reducing Agents In looking at oxidationreduction reactions, we can focus on the role played by a particular reactant in a chemical reaction. Dangerous goods label for oxidising agents In chemistry, an oxidizing agent (oxidant, oxidizer) is a substance that has the ability to oxidize other substances (cause them to lose electrons). HAZMAT Class 5 Oxidizing agents and organic peroxides bleaching agents, oxidizing and reducing agents, enzymes, and emulsifiers. Dangerous goods label for oxidising agents In chemistry, an oxidizing agent (oxidant, oxidizer) is a substance that has the ability to. Oxidizing agents make oxidation happen, and reducing agents make oxidation happen. And oxidizing agent takes electrons from something, allowing it to be oxidized, and a reducing agents gives. Let's see how to identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in a redox reaction. So here, we're forming sodium chloride from sodium metal and chlorine gas. And so before you assign oxidizing and reducing agents, you. Chemistry oxidizing and reducing agents oxidizing agent vs reducing agent. A chemical substance which reduces itself but oxidized other substance is known as the oxidizing agent. Br 2 is an oxidizing agent in the following reaction. reducing agents, and those of the electropositive elements are very strong reducing agents because the metal gives up electrons to the carbon, resulting in a polar MC bond with a partial positive charge on the metal and a negative charge on the carbon. The first step in determining which species is the oxidizing agent is to start by finding which reactant was reduced. Likewise, the molecule or element that is was oxidized is also the reducing agent. from Organic Chemistry by Robert C. Professor of Chemistry, emeritus Organic Oxidizing Agents (17. 2C) 1711 Ketones to Esters Aldehydes to Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols Alcohols from Organic Reducing Agents (17. 7B) 1730 Cannizzaro Reaction Chem 535 Synthetic Organic Chemistry Common Reducing Agents for the Conversion of Alcoholic, Carboxylic and NitrogenContaining Related Functionality Page 1. Strong oxidizing agents can present fire and explosive hazards. This hazard is highest when there is a possibility of an oxidizing agent coming in contact with a reducing agent, a fuel, or some other In organic chemistry, oxidationreduction really boils down to are we adding oxygens, are we adding hydrogens. Instead of looking at these complicated formulas and equations, we're really just going to be able to look at the molecule itself to tell if it's going to be oxidized or reduced. In chemistry, a reducing agent is an individual reactant in a reductionoxidation (redox) reaction that reduces another reactant by donating electrons to that reactant. The inclusion of a bibliography of reviews and monographs, a compilation of Organic Syntheses procedures with tested experimental details and references to oxidizing and reducing agents will ensure that this handbook is both comprehensive and convenient. Chemistry in terms of gain or loss of electrons understand the terms oxidation, reduction, redox, oxidising agent, reducing agent
Related Images:
- Bd 1280x720 avc aac
- 80s r b hits
- Jap loli
- Justice league of america 11
- The Pocket Book Of Old Masters
- Sanyo Mcd Z120 Mcd Z120f Service Manual Download
- American literature 8th edition
- Finger eleven falling on
- Yify christmas carol
- Libro Los Pasos Del Maestro Pdf
- SEE YOU AT THE TOP
- Bruno mars live
- Battle of tory
- Nl ebook esther verhoef
- Danni daniels danni daniels
- Finding joy 2018
- Dc new week 146
- Johnny cash wanted
- South park uncensor
- The Enigma of the Return
- 3rd birthday psp
- How To Install Air Bag On A Bmw 325i
- Farming Simulator Modding For Dummies
- Oculus mp4
- Fantastic four rise of the silver surfer wii
- Happy days s04
- Bending the rule
- When the heart emerges glisten
- Deep Learning Ian Goodfellow Pdf
- Rar serial
- Bobcat Hydraulic Charge Pressure Low
- Sound effects for video
- 720p tamil video songs
- LUDACRIS REST OF MY LIFE
- Game of thrones s01e01 subtitles
- Prison break french saison 1
- The dish 2000
- Dragon ball season 9
- Dog behavior training
- X64 pt br
- Road warrior 720p
- Bolne wali cat download music
- The hangover 2018 dual audio
- The new adventures of old christine s01e04
- Afrojack Ten Feet Tall david guetta
- Celestine bonne a tout faire 1974
- Elements Of Quantum Mechanics Fayer
- All matthews women read info dvf
- Cryostasis the sleep of reason
- The Movie Stars Red Hot Holiday Fling
- Le nombre 23 fr
- How to live parents
- Hart of dixie s3e19
- Fast five hin
- Vengeance Essential Clubsounds
- Yify 1080p 2000
- Cat stevens the very best
- The roly mo show
- Suicide Squad Amanda Waller
- Primate Diversity Edition 1
- Ravan 2010 dvdrip
- Mel kara de rabba
- Pink floyd welcome
- Hunger game fire 720p
- Foxit pdf editor key
- SLT Reverse Directory
- Iv
- Dial M for Murder
- Captain america 2018 024
- Poirot season 13
- Daily Reading And Writing Warm Ups 4th And 5th Grades
- Crack Para Logos 4
- Boss xvid s02e08