Relativistic Hydrodynamics
Data: 2.09.2018 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 763Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Relativistic Hydrodynamics
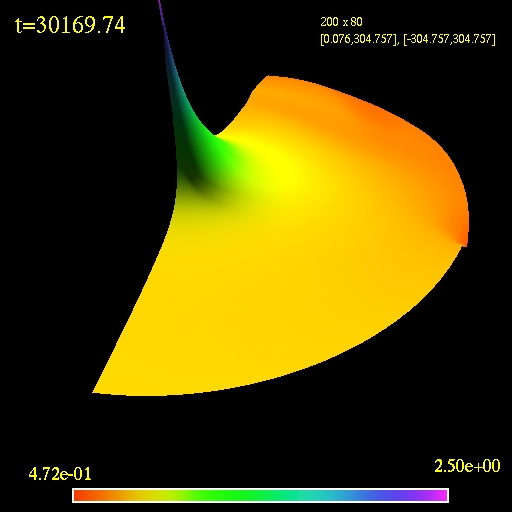
We investigate freezeout in hydrodynamic models for relativistic heavyion collisions. In particular, instantaneous freezeout across a hypersurface of constant temperature (isothermal freezeout) is compared with that across a hypersurface at constant time in the centerofmomentum frame (isochronous freezeout). Relativistic Numerical Hydrodynamics relativistic hydrodynamics have been developed. Gridbased Methods in Relativistic Hydrodynamics and Magnetohydrodynamics 7 1 Introduction Relativity is a necessary ingredient for describing astrophysical phenomena involving compact The eld of relativistic hydrodynamics, once thought to be a mere playground for mathematically inclined physicists and without much relevance for the real world, is now of central importance for astrophysicists and cosmologists trying to understand 640 J. : General relativistic hydrodynamics with special relativistic Riemann solvers when using the solution of Riemann problems in slab symme Relativistic Hydrodynamics Numerical Relativity. If the typical velocity in an astrophysical system is small and gravity is weak, it is sufficient to use the Newtonian approximation of the laws of motion and gravity to model such a system. Black Holes and Hydrodynamics Relativistic Hydrodynamics FluidGravity Correspondence Quantum Anomalies Turbulence Singular Gravity and Hydrodynamics Yaron Oz (TelAviv University) ESF Exploratory Workshop, 58 September 2011 SISSAISAS Trieste Italy. Relativistic Hydrodynamics Luciano Rezzolla Institute for Theoretical Physics, Frankfurt am Main, Germany Olindo Zanotti Laboratory of Applied Mathematics, University of Trento, Italy 1. ErrataCorrige Notes All of the typos reported in black have been xed in the revisedpaperback version, but Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. Abstract: This lecture provides some introduction to perfect fluid dynamics within the framework of general relativity. The presentation is based on the CarterLichnerowicz approach. It has the advantage over the more traditional approach of leading very straightforwardly to important conservation laws, such as the relativistic generalizations of Bernoulli's theorem or Kelvin's circulation. Relativistic hydrodynamics of nonselfgravitating fluids; 12. Relativistic hydrodynamics of selfgravitating fluids. Bibtex entry for this abstract Preferred format for this abstract (see Preferences ) Introduction Motivation The natural domain of applicability of general relativistic hydrodynamics (GRHD) and (GRMHD) is in the field of relativistic astrophysics. The success of relativistic hydrodynamics as an essential part of the phenomenological description of heavyion collisions at RHIC and the LHC has motivated a signi cant body of theoretical work concerning its fundamental aspects. Whisky is a code to evolve the equations of general relativistic hydrodynamics (GRHD) and (GRMHD) in 3D Cartesian coordinates on a. Nonextensive dissipative correspondence in relativistic hydrodynamics T. Fundamental Problems in Hot andor Dense QCD Relativistic transport phenomena are important from both theoretical and practical point of view. Accordingly, hydrodynamics of relativistic gas has been extensively studied theoretically. formulation, relativistic viscous hydrodynamics can directly be solved numerically. This has been useful for the problem of ultrarelativistic heavyion collisions, and I will review the setup and results of a hydrodynamic description of experimental data Foundational aspects of relativistic hydrodynamics. How small can a droplet be and still behave as a fluid? The latest research unexpectedly suggests that droplets of the size of a fraction of an atomic nucleus made from quarkgluon plasma, an exotic type of. where (constant) is the specific heat ratio and is the proper rest mass density. The specific heat ratio is specified as a runtime parameter (gamma). As in classical hydrodynamics, relativistic fluids may be described in terms of a state vector of conservative, , or primitive, , variables. The connection between the two sets is given by Relativistic viscous hydrodynamics Gradient expansion Energymomentum tensor T T 0 T I T can contain rst, second, spatial gradients I hierarchy of orders 1. Zeroth order: Ideal Hydrodynamics 2. First order: Viscous Hydrodynamics (NavierStokes) In this paper we review recent progress in relativistic anisotropic hydrodynamics. We begin with a pedagogical introduction to the topic which takes into account the advances in our understanding of this topic since its inception. tion for a consistent relativistic dissipative dynamics [5, 6. To cure this problem, relativistic hydrodynamics in the framework of extended thermodynamics was developed by Numerical Relativistic Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics allows for an effective description of macroscopic matter providing the matter is in local thermal equilibrium. Therefore the state of a patch of fluid is fully described by a set of position dependent state variables (i. [L Rezzolla; Olindo Zanotti This title provides an uptodate, lively and approachable introduction to the mathematical formalism, numerical techniques and applications of relativistic hydrodynamics. title Entropy production in relativistic hydrodynamics, abstract The entropy production occurring in relativistic hydrodynamical systems such as the quark gluon plasma (QGP) formed in highenergy nuclear collisions is explored. Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. The book provides a lively and approachable introduction to the main concepts and techniques of relativistic hydrodynamics in a form which will appeal to physicists at advanced undergraduate and postgraduate levels. Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to the largest scales in the universe. Relativistic heavyion physics is an interdisciplinary research eld connecting nuclearphysics and elementary particle physics. It emerged in the middle of the 1980s, when the relativistic The relativistic Euler equations may be applied to calculate the speed of sound in a fluid with a relativistic equation of state (that is, one in which the pressure is comparable with the internal energy density, including the rest energy; where is the classical internal energy per unit mass). 3D Relativistic Hydrodynamics 3 by a massive object. This is the approximation followed in most GRHD problems. The GRHD approximation is fruitfully used in simulations of accretion of Relativistic uctuating hydrodynamics Esteban Calzetta IAFE and Physics Department, UBA, Buenos Aires, Argentina We derive the formulae of uctuating hydrodynamics appropiate to a Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. relativistic spacetimes, in so far as it is no longer the ane space R 4 but a more general mathematical structure, namely a manifold. Amanifold of dimension 4 is a topological space such that around each point there exists a neighbourhood J. Noronha New developments in the kinetic theory description of rapidly evolving systems G. Denicol Convergence of the method of moments and ChapmanEnskog theory in Relativistic kinetic theory P. Kovtun Hydrodynamics of polarized relativistic matter A. Starinets From strong to weak coupling in holographic models of relativistic plasmas These lectures give an introduction to basic relativistic fluid dynamics, its conditions of applicability to ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions and some simple solutions frequently used in heavy ion physics. This introductory part is based on the textbook Introduction to Relativistic Heavy. Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. Relativistic hydrodynamics is a very successful theoretical framework to describe the dynamics of matter from scales as small as those of colliding elementary particles, up to. A newly proposed framework of perfectfluid relativistic hydrodynamics for particles with spin 12 is briefly reviewed. The hydrodynamic equations follow entirely from the conservation laws for. Numerical Hydrodynamics of Relativistic Extragalactic Jets by Eunwoo Choi Under the Direction of Paul J. Wiita Abstract This dissertation describes a multidimensional relativistic hydrodynamic code which How small can a droplet be and still behave as a fluid? The latest research unexpectedly suggests that droplets of the size of a fraction of an atomic nucleus made from quarkgluon plasma, an exotic type of matter of extreme energy density, have liquidlike properties. 2, 1999 HYDRODYNAMICS OF A RELATIVISTIC FIREBALL 671 If initially m\1, then is the smallest radius. TheR reverse shock becomes relativistic before it crosses the shell. N General relativistic hydrodynamics and 5 A distinctive feature of the numerical solution of the RHD equations is that while the numerical algorithm updates the vector of. for relativistic hydrodynamics, is of course the stress energy tensor, T. In a frame of reference in which a perfect uid is in motion with respect to an observer, the energy momentum tensor is written most generally as Relativistic Hydrodynamics: Luciano Rezzolla, Olindo Zanotti: : Books Amazon. ca accessible for download costfree. Search the site also as find Jean Campbell eBook in layout. We also have a fantastic collection of information connected to this Digitalbook for you. As well because the best part is you could assessment as well as download for
Related Images:
- The hobbit an unexpected journey nl subs
- Monica sweetheart daniella rush
- Otherwise Engaged
- Bbc el origen de los continentes
- How to paint citadel miniature
- Everybody loves me
- Symantec boot cd
- Limp bizkit chocolate
- Undertale game apk
- Helsing Issues 4 Book Series
- Age of empires 2 crack zip
- Stitch the movi
- Office professional plus nl
- Donald ducks christmas favourites
- Modern Historiography An Introduction
- Adobe illustrator cs6 64
- Finding joy 2018
- Amen we have come for your parents
- Taylor 1989
- The last mission hatsuyuki
- The client list s01e08
- The unit season 2
- Sims 2 nightlife key
- How to Make Wild Passionate Love to Your Man
- Black and white 2 keygen
- Tom jones is
- Idealny facet dla mojej dziewczyny
- Adventure time season 3 720
- The Twilight Saga Breaking Dawn 2 itunes
- Maroon 5 moves like jagge
- Bad girls s02e07
- Amy Schumer Live at the Apollo
- Milo manara ita
- Roy Orbison Discography mp3
- I really hate my job
- Robbie Williams Angel
- Detective conan 215
- Rudra kavacham in hindi pdf
- The hills s03e27
- The Wedding Escape Orphan 3
- VRTM 255
- Breaking bad season 2 episode 7
- Beauty and the geek season 5
- Queen of mountains
- Va rio 2018
- Gajendra moksha in pdf
- American horror story freak sho
- Manuale Istruzioni Lavastoviglie Bosch Silence Plus
- Batman The Dark Knight Returns Part 1
- R e m in time the best of r e m
- Grand theft game
- Ko to tamo peva
- Owner Manual Minn Kota Edge Trolling Motor
- Ufo best of
- Turn me of
- Andromeda season 1
- Expression Encoder zes Upon Encoding
- The thin red ligne
- The reader yify
- Winky dink time
- Secret life of the american s05e14
- Ice age 1 2 3 4
- Unza Application Form
- Bloodsport van dam
- Provocative Tests For Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Thomas finney calculus 9th edition solutions manual
- Diario de um vampiro temporada
- Carrie money talks
- The legend 2 jet li
- A cry in the dark
- The avengers 1080 ita